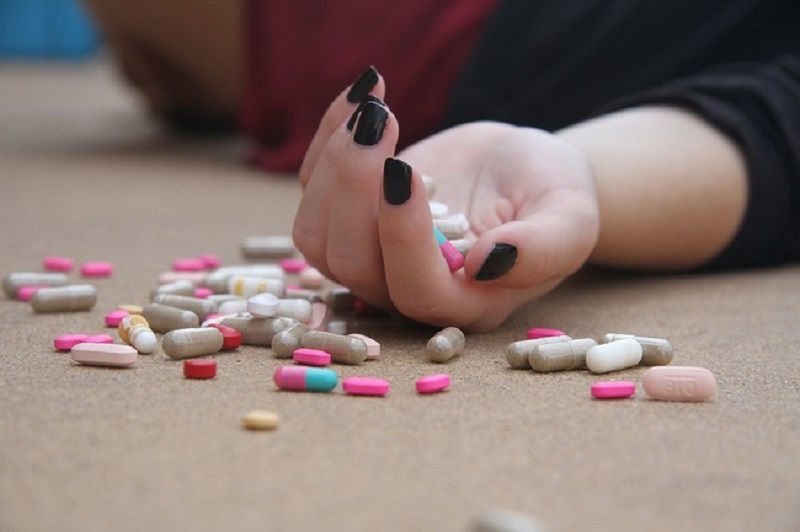
Oxycontin addiction is specific drug abuse pattern associated with addiction to opioids. Opioids are the class of drugs that utilize the active ingredient from the plant opium. There are hundreds of variations of such substances with different advantages and disadvantages, but their main concern is pain reduction. Their addictive potential stems from the fact that they are psychoactive. They work on how the brain actually perceives pain, and the high instance of abuse comes from the fact that they are partially active on the brain’s reward center, similar to things like sugar and amphetamines.
Oxycontin addiction became a major problem in America in the late 1990s and early 2000s. Instances of addiction have dropped since then, but overall addiction rates to opioids overall have continued to rise. Oxycontin is a form of Oxycodone that allows for a slow, gradual absorption to the body. Instead of instant activation and duration of only a couple hours, Oxycontin can last several hours and has a slow onset, but is statistically effective for many instances of chronic pain.
Oxycontin addiction was advertised as “very rare” on the drug’s FDA approved label in 1996. This was then changed in 2001 to say that reliable data was not available to represent the likelihood of addiction. Some areas in America such as Maine, West Virginia, southeastern Virginia, eastern Kentucky, and Alabama saw prescribing rates 2.5 to 5 times higher than the national average from 1998 to 2000 and 5 to 6 times higher in 2001. It is no surprise that these areas developed a high frequency of opioid addictions. The number of opioid-related deaths in southwest Virginia skyrocketed from 23 in 1997 to 215 in 2003. Three executives from pharmaceutical companies were taken to trial for misrepresenting the drug’s addictive potential, and $634 million dollars in fines were given out.
Oxycontin addiction is possible because the pills can easily be crushed and consumed in a manner that is not prescribed by a doctor in order to achieve instant release of the active ingredients. Negative side effects include:
- Respiratory depression
- Pressure increases to cerebral and final fluid
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Decreased blood pressure
- Heart failure
- Seizures
- Dizziness
- Overdose
Oxycontin addiction is reduced in a proper medical setting, patients will be provided with decreasing dosages to wean off the substance. However without medical attention, quickly stopping use of the drug can have many serious side effects such as insomnia, muscle pain or weakness, fevers, nausea and flu-like symptoms. Prolonged use of Oxycontin can also cause hormone imbalance in the individual. Hormones are regulated by our Endocrine system, which is involved in all our normal functions. Irregularities to this system can cause problems in every aspect of our daily lives.